Internationally, diamond grading is mainly assessed based on diamond weight, diamond color, diamond clarity and diamond cut. However, in addition to this, diamond fluorescence, milky light, caffeine, etc. are also included in the diamond grading criteria. This also has an impact on the price. Below is a perfect introduction to diamond grading standards and a detailed description of the diamond grading scale.
Diamonds are a standardized product. Its value is determined by the diamond grade, i.e. diamond weight, cut, color and clarity. Only diamonds evaluated by the strict 4C standards know their true value, and the GIA is undoubtedly the most authoritative in the world. Diamond grading is the 4C standard for diamonds, and the following are the criteria for diamond grading.
Weight (Carat)
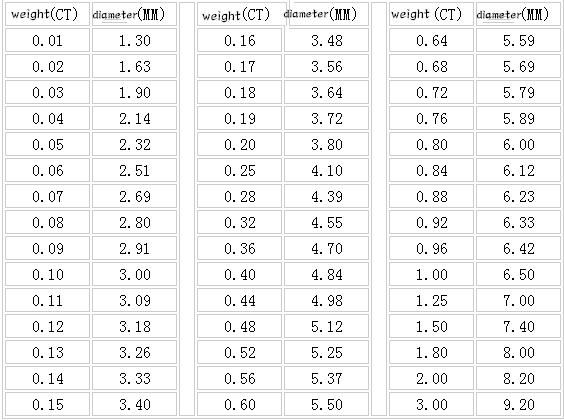
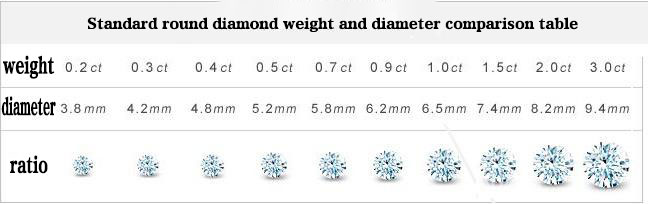
The weight of a diamond is measured in carats (CT). 1 carat = 0.2 grams = 100 points. 0.75 carats is also known as 75 points. As the weight of a diamond increases, the value of the diamond takes on an irregular geometric progression that consumers can determine based on their personal preferences and purchasing power. In general, only diamonds weighing more than 50 points begin to have collectible and investment value. Below is a table of the diameters corresponding to different diamond sizes.
Clarity
The clarity of a diamond refers to how much of the diamond is present. Most diamonds on the market contain very small, uncrystallized, fine carbon material. The smaller the number and size of the inclusions, the better the quality. Diamonds with this clarity are rarer and therefore less expensive. Not cheap. Internationally, diamond clarity grades are divided into six major categories, namely FL, IF, VVS, VS, SI, I, and can be further subdivided into several smaller grades.
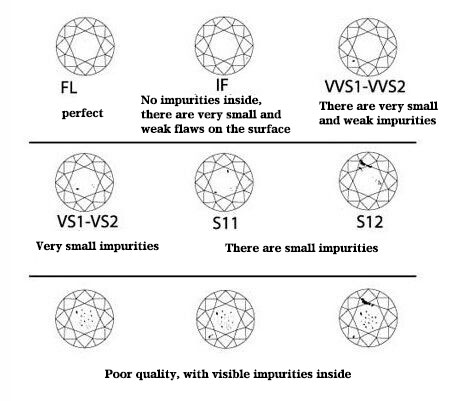
Diamond Clarity
FL means that the diamond is clean under 10x magnification, meaning that there are no inclusions on the inside or outside of the stone.
IF means that under 10x magnification, the diamond is free of flaws on the inside, but may have a little flaw on the surface, which can be removed by polishing.
VVS means that very small flaws can be seen in the pavilion or surface of the diamond when viewed under 10x gem loupe. the difference between VVS1 and VVS2 is that the latter has tiny cotton-like dots and stubble.
VS means that very small flaws can be seen when the diamond is viewed under a 10x gem loupe. the difference between VS1 and VS2 is that the latter may have tiny cotton dots or stubble.
SI means that flaws are easily visible when looking at the diamond under 10x loupe, but are not visible to the naked eye.
I1, I2 and I3 mean that small flaws are easily visible when viewing the diamond under 10x magnification. Some have visible cracks and fissures that can be easily seen with the naked eye.
All diamonds are viewed for clarity with a 10x loupe, and only I3 diamonds have flaws that are easily visible with the naked eye.




Color
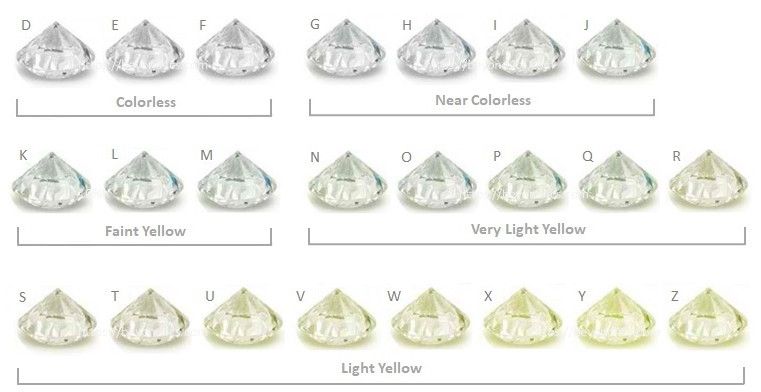
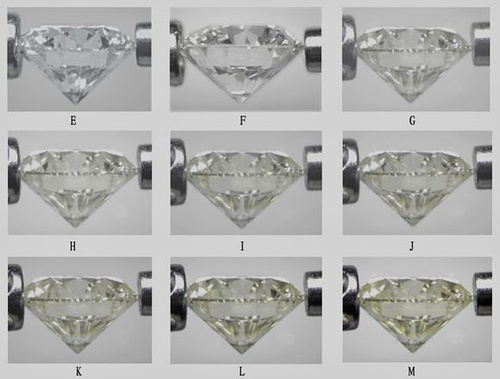
The color of a regular diamond ranges from completely colorless to yellow and brown. Among them, completely colorless diamonds are very rare and are the highest color grade among ordinary diamonds. Depending on the purity of the color, the color grades of diamonds in the world are divided by letters of the alphabet, starting from D and divided into D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N… The grade decreases in order.
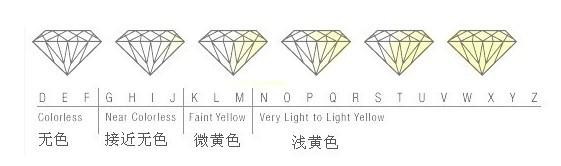
D grade: completely colorless. The highest color level, extremely rare!
E grade: colorless. Only gem identification experts can detect traces of color. It’s a very rare diamond
F grade: colorless. A small amount of color can only be detected by jewelry experts, but it is still considered colorless. Belongs to high-quality diamonds.
G-H grade: nearly colorless. When compared with higher color diamonds, there is a slight color. But diamonds of this color class still have a high value.
I-J grade: close to colorless. A slight color can be detected. The value is higher.
K-M grade: darker color, poor fire color.
N-Z grade: darker color, poor fire color.


Cut
The diamond cut is the only parameter of the diamond grade that can be manually controlled. The quality of the diamond cut determines the presentation of the diamond’s brilliance. A good cut can even cover up flaws and deficiencies in the diamond itself, so many consumers will have their diamonds cut. The work is the primary focus of a diamond purchase. Diamond cut grades are classified as excellent cut, very good cut, good cut, average cut and poor cut.
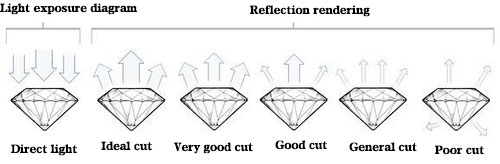
Very Fine: represents a standard that only 3% of first-class, high-quality diamonds can achieve. This cut allows the diamond to reflect almost all the light that enters the diamond. It is an elegant and outstanding cut.
Very Good. Represents approximately 15% of a diamond’s cut. It allows the diamond to reflect the light of a standard grade cut, but at a slightly lower price.
Good. Represents approximately 25% of the diamond’s cut. The diamond reflects most of the light that enters the diamond. It is much less expensive than the VG grade.
FAIR: Represents about 35% of the diamond cut, which is still a high quality diamond, but the average cut does not reflect light as well as the G grade cut.
POOR: This includes all diamonds that do not meet the general cut criteria. These are diamonds that are either deep and narrow or shallow and wide in cut, which tends to allow light to escape from the edges or the bottom, thus causing the diamond to lose its brilliance.

Fluorescence Intensity
Thirty-five percent of the world’s diamonds have a fluorescent effect. 97% of fluorescent diamonds emit blue fluorescence, making up the majority, with the remaining 3% being yellow, green, and red, and in between. Fluorescence of transitional colors, such as orange, blue-green, pink, etc. Fluorescence has no effect on the diamond itself, but in some cases it can affect the visual appearance of the diamond.
The intensity level of fluorescence is divided into four levels.” Very Strong”, “Strong”, “Moderate”, “Weak” and “None”. When fluorescence levels are at the “medium” or “strong” level, the diamond’s fluorescence adds a hazy or oily look to the diamond, making an almost colorless diamond surface appear whiter, and diamonds with medium or high fluorescence are less expensive than others.

Diamond Milk Caffeine
Milk is a cloudy aggregate of different colors in diamonds, usually white, but not infrequently gray and black. The white ones are usually referred to as “milk”. Its technical term is “cloud” and can affect the clarity and color of a diamond.
Coffee color is an abbreviation for coffee, brown (or tan). Coffee color often appears as a secondary color in primary colors such as yellow, orange, green, pink and red. Other colors include cape colored diamonds, except for the brown color in brown colored diamonds, which is a beneficial color. Intermediate colors are harmful colors, which will severely reduce the purity and brightness of the primary color.

The above is an introduction to each level. Buying a diamond is a matter of comprehensive consideration and personal preference. But there is only one purpose, to spend the least amount of money to get the most suitable diamond, but diamonds are after all luxury items that will not depreciate in value in the current situation. I’m here to make it clear that generally only high grade diamonds of 50 points or more have value retention! What I want to tell you here is that if you want to buy a diamond, you have to have enough money. These are the latest contents of diamond grade and diamond grade comparison table, so consumers can get it right!

You can contact our staff using the following methods:
Email :daikunjewelry@gmail.com
whatsapp: +1(551)5870742